6th millennium BC
| Millennia: |
7th millennium BC · 6th millennium BC · 5th millennium BC |
| Centuries: |
60th century BC · 59th century BC · 58th century BC · 57th century BC · 56th century BC · 55th century BC · 54th century BC · 53rd century BC · 52nd century BC · 51st century BC |
During the 6th millennium BC, agriculture spreads from the Balkans to Italy and Eastern Europe, and also from Mesopotamia to Egypt. World population is essentially stable at circa 5 million people, though some speculate up to 7,000,000.
Events
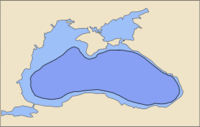
Black Sea today (light blue) and in 5600 BC (dark blue) according to Ryan's and Pitman's theories, versions of the Black Sea deluge theory

Byzantine Calendar illustrating 1 September 5509 BC.

Yangshao Culture
- c. 6000 BC: The Mehrgarh culture reaches its height c. 6000 BC. The Mehrgarh site is one of the most important Neolithic sites in the world. It is located in present-day Pakistan (Baluchistan Province).
- c. 6000 BC: The entire 6th Millennium was a part of the Holocene climatic optimum (so were the 4th, 5th, and 7th Millennia). This was a warm period also known as the Atlantic period. This period was characterized by minimal glaciation and high sea levels. (McEvedy)
- c. 6000 BC: Records of the Mosyllonian civilization in somalia
- c. 6000 BC: The Copper Age comes to the Fertile Crescent. (Roux 1980) First use of copper in Middle East. (Bailey 1973)
- c. 6000 BC: Fully Neolithic agriculture has spread through Anatolia to the Balkans. (1967 McEvedy)
- c. 6000 BC: Beginning of Neolithic Yangshao culture in south-central China <t.1500 BC>. Somewhere in this expanse of time, they invent the earliest pictographs of Chinese writing. (Atlas of China, 1983)
- c. 6000 BC: Equids disappear from the Americas.
- c. 6000 BC: Junglefowl kept in India.
- c. 6000 BC: Female figurines holding serpents are fashioned on Crete and may have been associated with water, regenerative power and protection of the home.
- c. 5900 BC: Prehistoric Vinca culture emerges on the shores of lower Danube.
- c. 5800 BC: Beginning of the Dadiwan culture in China.
- c. 5800 BC: The Hosanna Period in Mesopotamia <t. 5500 BC>, with the earliest version of stamp seals. (Roux 1980)
- c. 5760 BC: The volcano Puy-de-Dôme in France erupts.
- c. 5677 BC: Cataclysmic volcanic explosion of 12,000-foot (3,700 m) high Mount Mazama creates Oregon's Crater Lake[1] when the resulting caldera fills with water. With a Volcanic Explosivity Index of 7, it remains the largest single Holocene eruption in history of the Cascade Range.
- c. 5600 BC: Beginning of the desertification of North Africa, which ultimately lead to the creation of the Sahara desert. It's possible this process pushed some natives into migrating to the region of the Nile in the east, thereby laying the groundwork for the rise of Egyptian civilization.
- c. 5600 BC: The Red Paint People become established in the region from present-day Labrador to New York state.
- 5509 BC: The Byzantine calendar dates creation to 1 September of this year.
- c. 5500 BC: Beginning of the Xinle culture in China.
- c. 5500 BC: Agriculture started in Ancient Egypt.
- c. 5500 BC: Predynastic period (Neolithic) starts in Ancient Egypt (other date is 4350 BC).
- c. 5450 BC: Volcano Hekla eruption.
- c. 5400 BC: Beginning of the Zhaobaogou culture in China.
- c. 5400 BC: Irrigation and the beginning of the Sumerian civilization in Southern Iraq.
- c. 5400 BC: Watson Brake mound complex constructed in present-day Louisiana. (Correction: 5400 BP, or 3400 BC)
- c. 5300 BC: Beginning of the Beixin culture in China.
- c. 5200 BC: Beginning of human inhabitation and settlements in Malta.
- c. 5000 BC: Beginning of the Hemudu culture in China.
- c. 5000 BC: Beginning of the Daxi culture in China.
- c. 5000 BC: Beginning of the Majiabang culture in China.
- c. 5000 BC: Beginning of the Yangshao culture in China.
- c. 5000 BC: Farming reached central and north Europe.
Environmental changes
Holocene Epoch
|
|
| ↑ Pleistocene |
| Holocene |
- Preboreal (10.3 ka – 9 ka),
- Boreal (9 ka – 7.5 ka),
- Atlantic (7.5 ka – 5 ka),
- Subboreal (5 ka – 2.5 ka)
- Subatlantic (2.5 ka – present)
|
- c. 7000 BC: Beginning the Holocene climatic optimum.
- c. 6000 BC – The land bridge connecting England with the rest of Europe disappears beneath the waters of the North Sea and the English Channel.
- c. 5600 BC: According to the Black Sea deluge theory, the Black Sea floods with salt water. Some 3000 cubic miles (12,500 km³) of salt water is added, significantly expanding it and transforming it from a fresh-water landlocked lake into a salt water sea.
Inventions, discoveries, introductions
- c. 6000 BC: Cycladic people started to use a coarse, poor-quality local clay to make a variety of objects.
- c. 6000 BC: Brick building was taking place at Çatalhöyük, Turkey.[2]
- Agriculture appears in the valley of the Nile.
- Rice cultivated in Asia.
- Plough invented.
- c. 6000–5000 BC: Wine is created for the first time in Persia.
- c. 5000 BC: Agriculture began in the Americas perhaps this early, in complete isolation from the Old World.[2]
- Artifacts of stone were supplemented by those of metal, and the crafts of basketry, pottery, weaving (Africa).
- Dead were buried in a fetal position, surrounded by the burial offerings and artifacts, facing west (Africa).
- Decorated, black-topped clay pots and vases; bone and ivory combs, figurines, and tableware, are found in great numbers (Africa).
- Jewelry of all types and materials (Africa).
- Objects began to be made not only with a function, but also with an aesthetic value. (Africa)
- Organized, permanent settlements focused around agriculture. (Africa)
Cultural landmarks
References
- ↑ Zdanowicz, C. M.; Zielinski, G. A.; Germani, M. S. (1999). "Mount Mazama eruption; calendrical age verified and atmospheric impact assessed". Geology 27 (7): 621–624. doi:10.1130/0091-7613(1999)027<0621:MMECAV>2.3.CO;2. http://geology.geoscienceworld.org/cgi/content/abstract/27/7/621.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Roberts, J: "History of the World.". Penguin, 1994.
|
Millennia |
|
1st · 2nd · 3rd · 4th · 5th · 6th · 7th · 8th · 9th · 10th · 11th and beyond
11th BC and prior · 10th BC · 9th BC · 8th BC · 7th BC · 6th BC · 5th BC · 4th BC · 3rd BC · 2nd BC · 1st BC
|
|


